 |
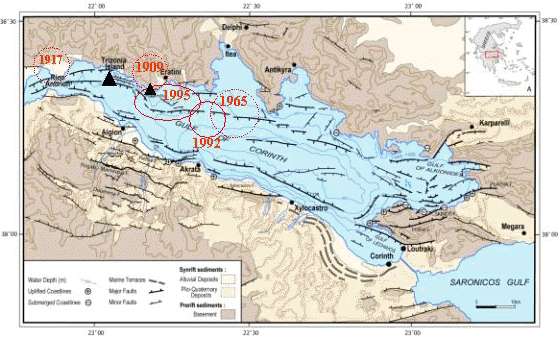
Scheme of Corinth gulf (after Moretti, 2003). Location of the main recent destructive earthquakes. Large and small black triangles indicate the location of Trizonia EM and Psaromita EM stations. |
The Corinth rift is a high seismic area frequently affected by seismic swarms. In the last 35 years five earthquakes of magnitude larger than 5.8 have occurred along the rift while a North-South extension of 1.5 cm per year is observed.
Two major earthquakes recently occurred at the western tip of the rift (Galaxidi, M 5.8 in 1992, Aigion, M 6.2 in 1995).
 |
Scheme of Corinth gulf (after Moretti, 2003). Location of the main recent destructive earthquakes. Large and small black triangles indicate the location of Trizonia EM and Psaromita EM stations. |
Several monitoring networks were progressively set through a European project (CRL; http://www.corinth-rift-lab.org/index_en.html) to better measure, model and predict the processes leading to earthquakes.
EM studies and monitoring stations supported by the CNES are set in this multi-parametric configuration in order to better constrain the processes generating EM signals associated with tectonic activity.
The main EM station is set on Trizonia island where the faults have not broken yet. At Psaromita a second station only records the low frequency EM field in order to discriminate the natural signals generated by the tectonic activity from the man-made noise.
The objective of such station is to record the magnetic and electric fields from 10 kHz to DC. This large frequency domain requires to implement different specific sensors, in particular magnetic ones. The architecture is the following:
A PC computer located on the field experiment and equipped with a 8 channels, 24 bits resolution analogue-digital board, controls the data acquisition as well as the time synchronisation with a GPS receiver (Global Positioning system). Large mass storage of 600 Mo is attached to the system.
On this PC computer data are measured during 55 minutes at 1 kHz and 5 minutes at 10 kHz, repeatedly:
Three orthogonal induction coils record the magnetic field in the VLF domain (frequency band of the sensors 0.3 kHz-30 kHz),
Three orthogonal induction coils record the magnetic field in the ELF domain (frequency band of the sensors 3 Hz-3 kHz)
Two horizontal buried electric lines of 50 m length record the electric field along the North-South and East-West direction.
On a second 24 bits autonomous system records the EM field at 40 Hz sampling and transfers data to the PC computer:
A fluxgate magnetometer records the three components of the magnetic field,
Two horizontal buried electric lines of 50 m length record the electric field along the North-South and East-West directions. The electric sensors are non polarizing lead-lead chloride (Pb-PbCl2) electrodes buried at about 1 m depth,
One 1 Hz vertical seismometer.
Far away of power lines the EM equipment is constrained to use high capacity batteries recharged by solar panels.
|
|
|
Construction of the EM station in Trizonia. The complete data acquisition system is in a hut.
The power supply is given by batteries recharged by solar panels.
In the front of the picture are the trenches in which the electric lines are buried.
A remote PC computer is set on the northern cost where power supply is available. The tasks of this computer are:.
To collect data from the field experiment PC computer by a WIFI connection,
To transfer some of the records by a satellite Internet bidirectional connection to the server set in the laboratory in France,
To implement data processing on the files not sent by Internet satellite.
|
|
Scheme of the location of the EM field station in Trizonia island and of the remote PC computer on the northern cost for data transfer by satellite Internet connection. A WIFI data transmission is used to send data from the field to the remote PC computer. |